Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (110), p.13 - 19, 2020/10
The article depicts how to estimate the external exposure dose for wild animals using electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. The relationship between the CO radical intensity and the absorbed dose, that is, dose response curve of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed, and the detection limit of our method was estimated. The estimated detection limit of 33.5 mGy is comparable to the previously reported detection limit for human molar teeth. The external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined using this dose response curve. The estimated external exposure dose were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
radical intensity and the absorbed dose, that is, dose response curve of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed, and the detection limit of our method was estimated. The estimated detection limit of 33.5 mGy is comparable to the previously reported detection limit for human molar teeth. The external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined using this dose response curve. The estimated external exposure dose were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Koarai, Kazuma; Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Osaka, Ken*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 134, p.106315_1 - 106315_4, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The relationship between the CO radical intensity and the absorbed dose (dose response curve) of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed by electron spin resonance and the detection limit of our system was estimated to be 33.5 mGy, which is comparable to the detection limit for human molar teeth. Using the dose response curve, external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined. The results suggest that the external exposure dose for the wild Japanese macaques were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
radical intensity and the absorbed dose (dose response curve) of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed by electron spin resonance and the detection limit of our system was estimated to be 33.5 mGy, which is comparable to the detection limit for human molar teeth. Using the dose response curve, external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined. The results suggest that the external exposure dose for the wild Japanese macaques were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
Kumada, Takayuki
Kagaku No Yoten Shirizu, 20, P. 71, 2017/06
no abstracts in English
Tokuyasu, Kayoko; Yasue, Kenichi; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Tamura, Itoko; Horiuchi, Yasuharu
QST-M-2; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2015, P. 189, 2017/03
Understanding the stage of mountain building is crucial to the stability assessment of geological environments in geological disposal system. In this context, we have carried out the research and development of provenance analysis techniques to elucidate the mountain-building stage. Here we present the results focusing on the R&D using the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) signals from quartz in sediments and their basement rocks.
 -ray irradiated amino acids
-ray irradiated amino acidsNagata, Natsuki*; Komoda, Seiichi*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Nakamura, Hideo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ukai, Mitsuko*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 103, 2016/02
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Toru; Hijii, Keigo*; Okubo, Susumu*; Ota, Hitoshi*; Nakano, Hiroki*; Miyashita, Seiji*
Applied Magnetic Resonance, 46(9), p.997 - 1002, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.49(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)The S=1/2 kagome-lattice antiferromagnet is investigated by the numerical diagonalization of 18-spin finite-size cluster. The matrix elements proportional to the intensity of the singlet-triplet ESR transition are calculated in the presence of the Dzyaloshinsky-Moriya interaction. Some angle-dependent selection rules is also proposed.
Kikuchi, Masahiro; Ukai, Mitsuko*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 89, 2015/03
Kishida, Keigo*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Nakamura, Hideo*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ukai, Mitsuko*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 90, 2015/03
 100
100 systems
systemsFujieda, Shinji*; Miura, Yoshinao*; Saito, Motofumi*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Microelectronics Reliability, 45(1), p.57 - 64, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:51.37(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To characterize the interface defects that are responsible for the negative-bias temperature instability (NBTI) of a thin plasma-nitrided SiON/Si system, we carried out inerface trap density measurements, electron-spin resonance spectroscopy and synchrotron radiation XPS. The NBTI was shown to occur mainly through the dehydrogenation of the interfacial Si dangling bonds (P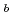 defects). Although we suggest that non- P
defects). Although we suggest that non- P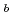 defects are also generated by the negative-bias temperature stress, nitrogen dangling bonds do not seem to be included. The plasma-nitridation process was confirmed to generate sub-oxides at the interface and thus increase the interface trap density. Furthermore, it was found that the nitridation induces another type of P
defects are also generated by the negative-bias temperature stress, nitrogen dangling bonds do not seem to be included. The plasma-nitridation process was confirmed to generate sub-oxides at the interface and thus increase the interface trap density. Furthermore, it was found that the nitridation induces another type of P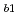 defect than that at pure-SiO
defect than that at pure-SiO /Si interfacec. Such an increase and structural change of the interfacial defects are likely the causes of the nitridation-enhanced NBTI.
/Si interfacec. Such an increase and structural change of the interfacial defects are likely the causes of the nitridation-enhanced NBTI.
Kolezhuk, A. K.*; Glazkov, V. N.*; Tanaka, Hidekazu*; Osawa, Akira
Physical Review B, 70(2), p.020403_1 - 020403_4, 2004/07
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:83.59(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Recently measured high-field ESR spectra of the spin dimer material TlCuCl are described within the framework of an effective field theory. A good agreement between the theory and experiment is achieved, for all geometries and in a wide field range, under the assumption of a weak anisotropy of the interdimer as well as intradimer exchange interaction.
are described within the framework of an effective field theory. A good agreement between the theory and experiment is achieved, for all geometries and in a wide field range, under the assumption of a weak anisotropy of the interdimer as well as intradimer exchange interaction.
Oshima, Takeshi; Morishita, Norio; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Isoya, Junichi*; Baba, Shinichi; Aihara, Jun; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Ishihara, Masahiro
Proceedings of OECD/NEA 3rd Information Exchange Meeting on Basic Studies in the Field of High Temperature Engineering (OECD/NEA No.5309), p.197 - 202, 2004/00
For the application of SiC to electronic devices, it is necessary to develop the fabrication technique of high quality SiC substrates with uniform carrier concentration. Since phosphorus (P) atoms become shallow donors in SiC, nuclear transmutation doping (NTD) is thought to be a good method for the fabrication of n-type SiC substrates with uniform electron concentration. However, defects are also introduced in SiC by neutron irradiation. Although thermal annealing at high temperatures above 1500 C is carried out to remove defects after irradiation, heavy damage in SiC is hard to recover. Therefore, the process for the reduction of defects in SiC irradiated with neutrons is necessary to develop. In this study, neutron irradiation into SiC at elevated temperature was carried out to decrease radiation damage. The electrical properties of the samples are studied using Hall effect measurement. Furthermore, to establish the measurement technique for the estimation of P atoms created in SiC by NTD, P atoms in SiC were investigated using Electron Spin Resonance (ESR).
C is carried out to remove defects after irradiation, heavy damage in SiC is hard to recover. Therefore, the process for the reduction of defects in SiC irradiated with neutrons is necessary to develop. In this study, neutron irradiation into SiC at elevated temperature was carried out to decrease radiation damage. The electrical properties of the samples are studied using Hall effect measurement. Furthermore, to establish the measurement technique for the estimation of P atoms created in SiC by NTD, P atoms in SiC were investigated using Electron Spin Resonance (ESR).
Kumada, Takayuki
Physical Review B, 68(5), p.052301_1 - 052301_4, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:81.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Effect of pressure on the recombination of H atoms produced by UV-photolysis of O -doped solid H
-doped solid H was studied using ESR spectroscopy. The recombination rate constant was independent of pressure up to 13 MPa below 4.2 K, whereas it remarkably decreases with the increase in pressure above. The absence of pressure effect indicates that the H atoms do not diffuse by the physical exchange of positions with neighboring H
was studied using ESR spectroscopy. The recombination rate constant was independent of pressure up to 13 MPa below 4.2 K, whereas it remarkably decreases with the increase in pressure above. The absence of pressure effect indicates that the H atoms do not diffuse by the physical exchange of positions with neighboring H molecules, but by the tunneling reaction H + H
molecules, but by the tunneling reaction H + H
 H
H + H.
+ H.
Isoya, Junichi*; Oshima, Takeshi; Oi, Akihiko; Morishita, Norio; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 206, p.965 - 968, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Asano, Yoshihiro
Hoshako, 16(2), p.120 - 122, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Iwasaki, Midori*; Miyazawa, Chuzo*; Hamada, Tatsuji*; Funabiki, Jun*; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 103(2), p.125 - 130, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.64(Environmental Sciences)Absorbed dose to tooth enamels against external photon exposure was examined by the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dosimetry using tooth samples placed in a realistic physical phantom. Dose to teeth region was also measured with thermo-luminescence dosimeters (TLDs). A voxel-type phantom was constructed from CT images of the physical phantom. Monte Carlo calculations with this voxel-type phantom were performed to analyse the results of the experiments. The obtained data in this study were compared to the enamel doses, which were calculated with a modified MIRD-type and already given in a previous paper. The results suggested that the conversion factors from enamel dose to organ doses obtained by the modified MIRD-type phantom are to be applicable for retrospective individual dose assessments by the ESR dosimetry. The analysis, however, indicated that the size and figure of the head can affect the enamel dose for low photon energy region below 100keV.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
Radiation Risk Assessment Workshop Proceedings, p.71 - 78, 2003/00
Conversion from tooth enamel dose to organ doses against external photon exposure were studied in order to develop a method that can retrospectively estimate organ doses by the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dosimetry using tooth samples. Monte Carlo calculations using EGS4 code were performed to obtain dose to tooth enamel and organ doses by using a modified MIRD-type phantom. The Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dosimetry using tooth samples and dose measurements using thermo-luminescence dosimeters (TLDs) were also carried out to examine dose to teeth region with a realistic physical phantom. A Voxel-type phantom was constructed from CT images of the physical phantom. Monte Carlo calculations with the Voxel-type phantom were performed to verify the results of the experiments and enamel doses calculated by use of the modified MIRD-type phantom. The obtained data are to be useful for the retrospective assessment of individual dose in past exposure events by the ESR dosimetry with tooth enamel.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Iwasaki, Midori*; Miyazawa, Chuzo*; Hamada, Tatsuji*; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(9), p.964 - 971, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)Conversion from tooth enamel dose to organ doses was analyzed to establish a method of retrospective individual dose assessment against external photon exposure by the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dosimetry. Dose to tooth enamel was obtained by Monte Carlo calculations using a modified MIRD-type phantom. The calculated tooth enamel doses were verified by measurements with thermo-luminescence dosimeters inserted in a physical head phantom. Energy and angular dependences of tooth enamel dose were compared with those of other organ doses. Additional Monte Carlo calculations were performed to study the effects of human model on the tooth enamel dose with a voxel-type phantom, which was based on CT images of the physical phantom. The data derived with the modified MIRD-type phantom were applied to convert from tooth enamel dose to organ doses against external photon exposure in a hypothesized field, where scattered radiations were taken into account. The results indicated that energy distribution of photons incident to a human body should be required to evaluate precisely individual dose by the ESR dosimetry using teeth.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Saito, Kimiaki; Iwasaki, Midori*; Miyazawa, Chuzo*; Hamada, Tatsuji*; Funabiki, Jun*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.2), p.1314 - 1317, 2002/08
An analysis of dose to tooth enamel was carried out to develop a method that can predict the organdose and effective dose by the Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) dosimetry using teeth for external photon exposure. Absorbed dose to tooth enamel were obtained with Monte Carlo calculations using EGS4 code with a mathematical human model, which has a newly defined teeth-part. Experiments were also carried out to investigate the dose at the tooth area with a physical head phantom. The calculated doses to tooth enamel were, however, less than the measured doses with the TLDs for the case of photon incidence from the back of a human body. Then, a computational human model, called a “Voxel (Volume-pixel) type" phantom was constructed based upon a computed topography (CT) image of the physical head phantom used in the experiments.The additional Monte Carlo calculations were performed to verify the results in the experiments with the EGS4 in conjunction with user's code UCPIXEL and the Voxel type phantom.
 SOS-regulated UmuD
SOS-regulated UmuD protein
proteinSutton, M. D.*; Guzzo, A.*; Narumi, Issei; Costanzo, M.*; Altenbach, C.*; Ferentz, A. E.*; Hubbell, W. L.*; Walker, G. C.*
DNA Repair, 1(1), p.77 - 93, 2002/01
UmuD protein is a regulatory subunit of
protein is a regulatory subunit of  DNA polymerase V. This protein forms a complex with UmuC protein, a catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase V, and plays a important role in error-prone translesion DNA synthesis, which serves as the mechanistic basis for most DNA-damaging agent and UV light mutagenesis. In this paper, based on the results of a combination of experimental studies, we have developed a refined model for the structure of the UmuD
DNA polymerase V. This protein forms a complex with UmuC protein, a catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase V, and plays a important role in error-prone translesion DNA synthesis, which serves as the mechanistic basis for most DNA-damaging agent and UV light mutagenesis. In this paper, based on the results of a combination of experimental studies, we have developed a refined model for the structure of the UmuD homodimer. Implications of the structural change of UmuD
homodimer. Implications of the structural change of UmuD protein with respect to its roles in managing the action of DNA polymease V are discussed.
protein with respect to its roles in managing the action of DNA polymease V are discussed.
Kumada, Takayuki; Sakakibara, Masahiro*; Nagasaka, Toshimitsu*; Fukuta, Hiroya*; Kumagai, Jun*; Miyazaki, Tetsuo*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 116(3), p.1109 - 1119, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:77.99(Chemistry, Physical)We have studied diffusion and recombination of H atoms in solid hydrogen using ESR, ENDOR, and ESE spectrometer. The rate constant for recombination of H atoms in highly purified parahydrogen was found to be much smaller than that expected by diffusion coefficient. This result indicates that the H atoms do not recombine in the absence of energy dispersion path in highly purified parahydrogen.